
A 10-foot power strip is one of those simple, essential tools that makes a world of difference in office workstations. It gives you the length you need to safely connect multiple devices without yanking on cords or creating a spaghetti monster of trip hazards. With that extra reach, you gain a ton of flexibility in where you place your desks, leading to a much cleaner and more efficient workspace by bringing power right where it’s needed. At Cubicle By Design, we see how this small detail can transform an office layout.
Why Your Office Needs a 10-Foot Power Strip
We’ve all seen it. The distance between a desk and the nearest wall outlet can sometimes feel like a canyon. This is when employees start getting creative—and not in a good way. They’ll stretch standard-length cords across walkways or, even worse, plug multiple power strips into each other. These “solutions” are not just messy; they’re serious safety risks.
This is exactly where the strategic advantage of a 10-foot power strip comes into play. It’s more than just a longer cord; it’s a foundational piece for building a safe, organized, and truly productive office environment.
The biggest benefit is immediate flexibility. With ten feet of cable, you can finally arrange workstation cubicles and desks based on how your team actually works, not just where the outlets are. This simple change eliminates cord tension, cuts down on the risk of accidental unplugging, and neatly contains cables, preventing those hazardous tangles that cause trips and falls. A well-placed power strip is a surprisingly big part of an ergonomic setup. For more ideas on this, check out our guide on how to maximize the ergonomics of your office.
Solving Common Power Distribution Headaches
For any office or facilities manager, a long power strip solves a handful of persistent problems. Think of it as the simple, elegant answer to the logistical headaches that come with powering a modern, dynamic workspace.
- Puts an End to “Daisy-Chaining”: Plugging power strips into one another is a major code violation and a genuine fire hazard. A 10-foot cord provides the necessary reach to connect directly and safely to the wall outlet.
- Clears Away Trip Hazards: By running the cord neatly along walls or tucked under desks, the extra length keeps high-traffic walkways clear and safe for everyone.
- Supports Flexible Office Layouts: As teams grow and priorities shift, furniture needs to move. A longer power strip allows you to reconfigure your space without calling in an electrician to relocate outlets.
- Protects Your Valuable Equipment: Many models come with built-in surge protection, which is critical for safeguarding computers, monitors, and other sensitive electronics from damaging voltage spikes.
The widespread use of these devices really highlights their importance. In 2024, common power strips, including 10-foot models, grabbed a dominant market share of about 56.7% of the industry’s revenue, a trend driven by their sheer affordability and versatility. Read the full research about power strip market trends.
Ultimately, picking up a few high-quality 10-foot power strips is a small investment that pays you back in a big way through improved safety, organization, and operational agility. It’s a non-negotiable component for any business looking to create a smarter workspace. We know from experience that smart power management is the unsung hero of a well-designed workplace.
Getting to Grips with Power Strip Specs
Choosing the right 10-foot power strip can feel like trying to decipher a secret code. You’ll see terms like amps, joules, and UL ratings thrown around, but what do they actually mean for your office? Getting these details right is about more than just convenience; it’s critical for protecting your expensive equipment and preventing dangerous electrical overloads.
Think of your office’s electrical system like the plumbing in your house. The specs on a power strip are just telling you how much electrical “current” can flow through it safely. Once you understand a few key concepts, you can confidently pick a power strip that can handle the real demands of a modern workspace.
This infographic neatly summarizes the common power challenges that a well-chosen power strip can solve, focusing on safety, efficiency, and flexibility.
As you can see, a quality power strip is more than just an extension cord. It’s a central hub that addresses these key pain points, creating a much more stable and productive work environment.
Power Strip Technical Specifications Explained
Let’s break down the jargon you’ll find on the packaging. This table cuts through the noise and tells you exactly what to look for.
| Specification | What It Means | Recommended for Office Use |
|---|---|---|
| Amperage (Amps) | The maximum electrical current the strip can safely handle. | Standard is 15 amps. This is suitable for most workstation setups. |
| Voltage (Volts) | The “pressure” of the electrical circuit. In the U.S., this is always 120V for standard outlets. | 120V is the U.S. standard. |
| Joule Rating | How much energy the surge protector can absorb from a power spike. A higher number means better protection. | Look for at least 600 joules. For workstations with high-end computers, 1,000+ joules is even better. |
| UL Listing | A certification from Underwriters Laboratories, an independent safety science company. | Non-negotiable. Only buy power strips that are UL Listed or ETL Listed to ensure they meet safety standards. |
These four specs are your North Star when shopping. If a power strip meets the recommendations above, you’re on the right track.
Amps: The Real Bottleneck
Let’s stick with that plumbing analogy. If electricity is water flowing to your computer, then:
- Voltage is the water pressure. In the U.S., it’s a steady 120 volts. You don’t need to worry much about this number.
- Amperage (Amps) is the flow rate—how much water is actually moving through the pipe. This number is critical.
Most office power strips are rated for 15 amps. The danger comes when you plug in too many devices that draw a lot of current, like multiple high-performance PCs, large monitors, and maybe a laser printer. Exceeding that 15-amp limit is like forcing too much water through a small pipe. It causes the strip to overheat, creating a serious fire hazard.
How to Calculate Your Power Needs
So, how do you avoid overloading a 10-foot power strip? It’s simple math. The amperage draw is usually printed right on the power adapter or on a sticker on the back of each device. Just add up the amps for everything you plan to plug into a single strip.
As a solid rule of thumb, the total amperage of all your devices should never exceed 80% of the power strip’s rating. For a typical 15-amp strip, that means you should keep the total load under 12 amps to be safe.
Can’t find the amps? Look for the wattage (W). You can figure out the amps with a quick calculation: Watts / 120 Volts = Amps. For example, a 240-watt computer monitor will draw 2 amps (240 / 120 = 2). This easy check ensures all the equipment in your workstations operates well within safe limits.
Joules and UL Listings: Your Safety Nets
Beyond just delivering power, two other specs are absolutely non-negotiable for any office: surge protection and safety certification.
- Joule Rating: Think of this as the strength of a shield protecting your electronics. A joule rating tells you how much energy a surge protector can absorb before it fails. A sudden power spike can fry sensitive computer components instantly, so a higher joule rating means better protection. For an office with valuable equipment, look for a rating of at least 600 joules—though more is always better.
- UL Listing: This is arguably the most important safety feature of all. A UL (Underwriters Laboratories) mark means the power strip has been independently tested and certified to meet rigorous safety standards for its wiring, materials, and construction. An unlisted power strip is a total gamble. There’s no guarantee it was built with fire-resistant materials or can actually handle the load it claims to.
Choosing the right equipment can feel a bit overwhelming, but breaking it down makes it perfectly manageable. For a wider view on outfitting your space, our comprehensive office furniture buying guide offers even more valuable insights. Making an informed choice on something as simple as a 10-foot power strip is a small step that pays huge dividends in office safety and efficiency.
Smart Placement and Cable Management Strategies
So you’ve got a 10 foot power strip. That’s a great start, but its real magic isn’t just the outlets—it’s the freedom that long cord gives you. With a little strategic thinking, you can go from a tangled, hazardous mess to a clean, professional, and efficient workspace. The whole idea is to get power exactly where you need it while making the cords themselves practically disappear.
This is where you shift from just having the right tool to using it like a pro. Instead of letting wall outlets dictate your office layout, you’re now in control, placing desks and equipment based on workflow, not cord length. That extra reach is your ticket to a much cleaner and safer setup, helping you dodge the dangerous practice of “daisy-chaining” power strips and keeping walkways clear of trip hazards.
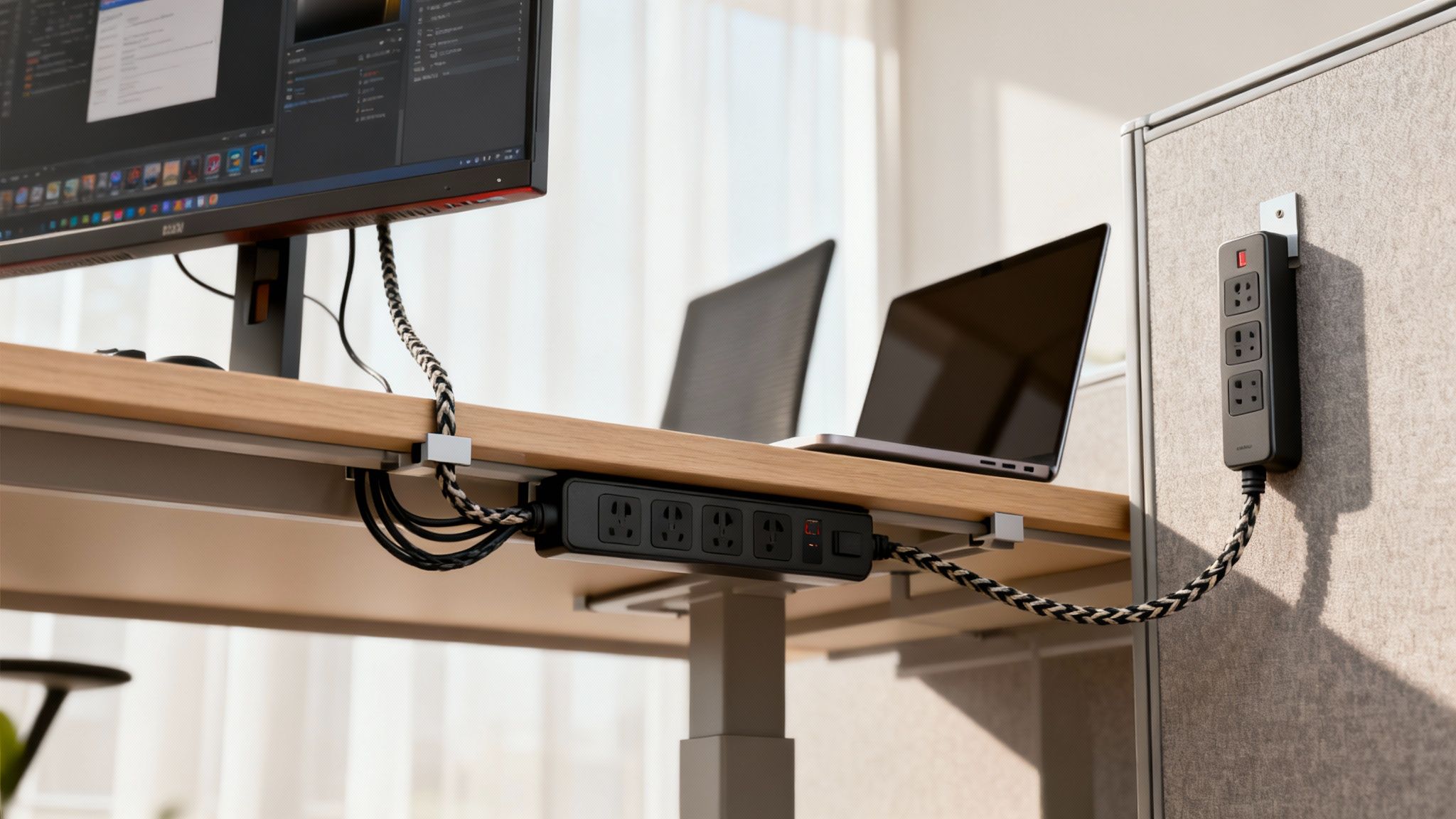

Finding the Perfect Mounting Spot
Let’s be honest: the best place for a power strip is usually out of sight. When you hide the power source, you cut down on visual clutter, which helps create a more focused, less distracting atmosphere. Luckily, there are a few tried-and-true ways to mount them that work perfectly with modern office furniture.
- Under-Desk Mounts: This is hands-down the most popular and effective method. By securing the 10 foot power strip to the underside of a desk, you create a central, hidden power hub. Cords for monitors, computers, and phone chargers can all be plugged in discreetly, leaving only the main cord to run neatly to the wall. We have a whole guide on how to set up an under desk power strip if you want to dive deeper.
- Vertical Panel Mounting: In a cubicle setup, those vertical panels are prime real estate. Mounting a strip vertically on a cubicle wall or leg keeps outlets easily accessible without hogging any desk space. It’s a great solution for shared workstations or any spot where people need to plug and unplug things often.
- Inside Cable Trays: A lot of modern desks and cubicle systems come with built-in cable trays or raceways. A slim power strip can often be tucked right inside these channels, keeping it completely hidden while delivering power along the length of the desk.
Taming the Cable Chaos
Once the power strip is mounted, the final step is wrangling all the cords that connect to it. This is what really gives your workspace that polished, professional look. It’s amazing what a few simple accessories can do to transform a tangled bird’s nest of wires into something clean and organized.
Think of it as the finishing touch that ties the whole setup together. A few minutes spent here will pay off big time in both looks and long-term safety.
The demand for flexible power solutions like the 10 foot power strip is growing rapidly. Driven by trends like remote work and automation, the global market for power and extension cords is projected to grow at an annual rate of about 10.1% from 2025 to 2032. This reflects a clear need for longer, more versatile power options in all types of workplaces. Discover more insights about these electrical industry trends.
Consider these simple but incredibly effective tools to finish the job:
- Cable Clips: These little adhesive clips are a lifesaver. Stick them to the underside of the desk or along the legs to guide cords neatly from your devices to the power strip.
- Velcro Straps or Zip Ties: Perfect for bundling up any excess cable. This stops long loops of cord from dangling down where they can get snagged or just look messy.
- Cable Sleeves: For the cleanest possible look, a fabric or plastic sleeve can wrap around multiple cords running in the same direction, turning them into one tidy tube.
By combining a 10 foot power strip with these simple cable management tricks, you can create a truly streamlined workspace. You can even map out your ideal layout and power distribution with our interactive Cubicle Designer tool to see how it will all come together.
Ensuring Office Safety and Electrical Code Compliance
While a 10 foot power strip is an incredibly handy tool for office flexibility, it comes with some serious responsibilities. Safety isn’t just a friendly suggestion; it’s a legal and ethical duty to protect your employees and your business. For any office manager, getting a handle on the basic rules of electrical code compliance is absolutely non-negotiable.
If you remember one thing, make it this: power strips are designed for temporary use only. They are not, and never should be, a substitute for permanent wiring. Using them as a long-term solution to snake a cord across the room to a distant outlet is a direct violation of guidelines from organizations like OSHA and the National Electrical Code (NEC). Why? Because over time, that prolonged use dramatically increases the risk of cord damage, overheating, and fire.
This distinction is crucial. A power strip is perfect for setting up a temporary project desk or for a visiting employee who needs to plug in their laptop. But if a workstation is a permanent fixture in your office, like our private office cubicles, it needs a permanent power source—installed by a qualified electrician—to keep things safe and compliant.
Key Electrical Code Guidelines to Follow
Trying to navigate electrical codes can feel a bit overwhelming, but a few core principles will keep your office out of trouble. These rules are put in place to prevent the most common—and most dangerous—electrical hazards you see in a commercial space.
Following these standards protects your team and can save you from costly fines or even a denied insurance claim if an incident occurs. It’s a fundamental part of managing any office responsibly. For a deeper look at professional setups, you might find our expert guide to office furniture installation useful, as it touches on many related safety topics.
Here are the non-negotiable rules for using any power strip in your workplace:
- Never Plug a Power Strip Into Another Power Strip: We’ve all seen it, but this practice, known as “daisy-chaining,” is strictly forbidden. It’s an easy way to overload the first strip and the wall outlet, creating a major fire risk.
- Do Not Run Cords Under Rugs or Carpets: Covering a power strip cord traps heat. It also hides any fraying or damage, turning a small, fixable issue into a hidden danger.
- Avoid High-Wattage Appliances: Power strips are meant for low-power devices like computers, monitors, and phone chargers. Never plug in space heaters, coffee makers, or microwaves. They draw way too much current and can easily cause the strip to overheat.
- Use Only UL or ETL Certified Strips: Make sure every 10 foot power strip has a certification mark from a recognized safety organization like Underwriters Laboratories (UL). This is your proof that it’s been properly tested for safety.
Actionable Checklist for Regular Inspections
Being proactive is your best defense against electrical accidents. A simple, routine inspection can help you spot the signs of wear and tear before they become serious problems. This check should be done at least twice a year and any time you reconfigure a workstation.
Use this quick checklist to see how your power strips are holding up:
- Inspect the Cord: Look for any cracks, fraying, or exposed wires along the entire ten-foot cord. If you find any damage, replace the strip immediately.
- Check the Plugs: Make sure the plug’s prongs are straight and secure. A loose or bent prong can create a bad connection and generate dangerous heat.
- Examine the Casing: Look for any signs of melting, strange discoloration, or cracks on the power strip’s plastic housing. A hot or discolored outlet is a serious red flag.
- Test the Outlets: When you plug something in, does it fit snugly? Loose connections can cause electrical arcing, which is a significant fire hazard.
Investing in high-quality, certified products isn’t just a good idea—it’s essential for protecting your people and your business. With our growing reliance on electronics, safe power distribution has never been more critical.
The global power strip market, which includes essential devices like the 10 foot power strip, was valued at approximately USD 13.43 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach about USD 22.30 billion by 2034. This growth is a direct result of the increasing number of electronic devices used in commercial and residential settings worldwide. Learn more about the power strip market findings here.
By prioritizing safety and sticking to the established codes, you can enjoy the convenience of a 10 foot power strip without putting your workplace at risk. It’s a simple but vital part of responsible facility management.
Integrating Power Strips with Your Cubicle System
A well-designed office isn’t just a collection of furniture; it’s a fully functional ecosystem where every single piece works in harmony. Think of a 10-foot power strip as the final, flexible link in a much bigger power distribution chain, perfectly complementing the structured electrical systems already built into your office furniture.
It helps to imagine your office’s power grid like a city’s road system. The building’s permanent wiring is the main highway, and the integrated power options inside your cubicle systems are the major streets branching off from it. Together, they form the backbone of your office’s electrical infrastructure, designed from the ground up for safety and efficiency.
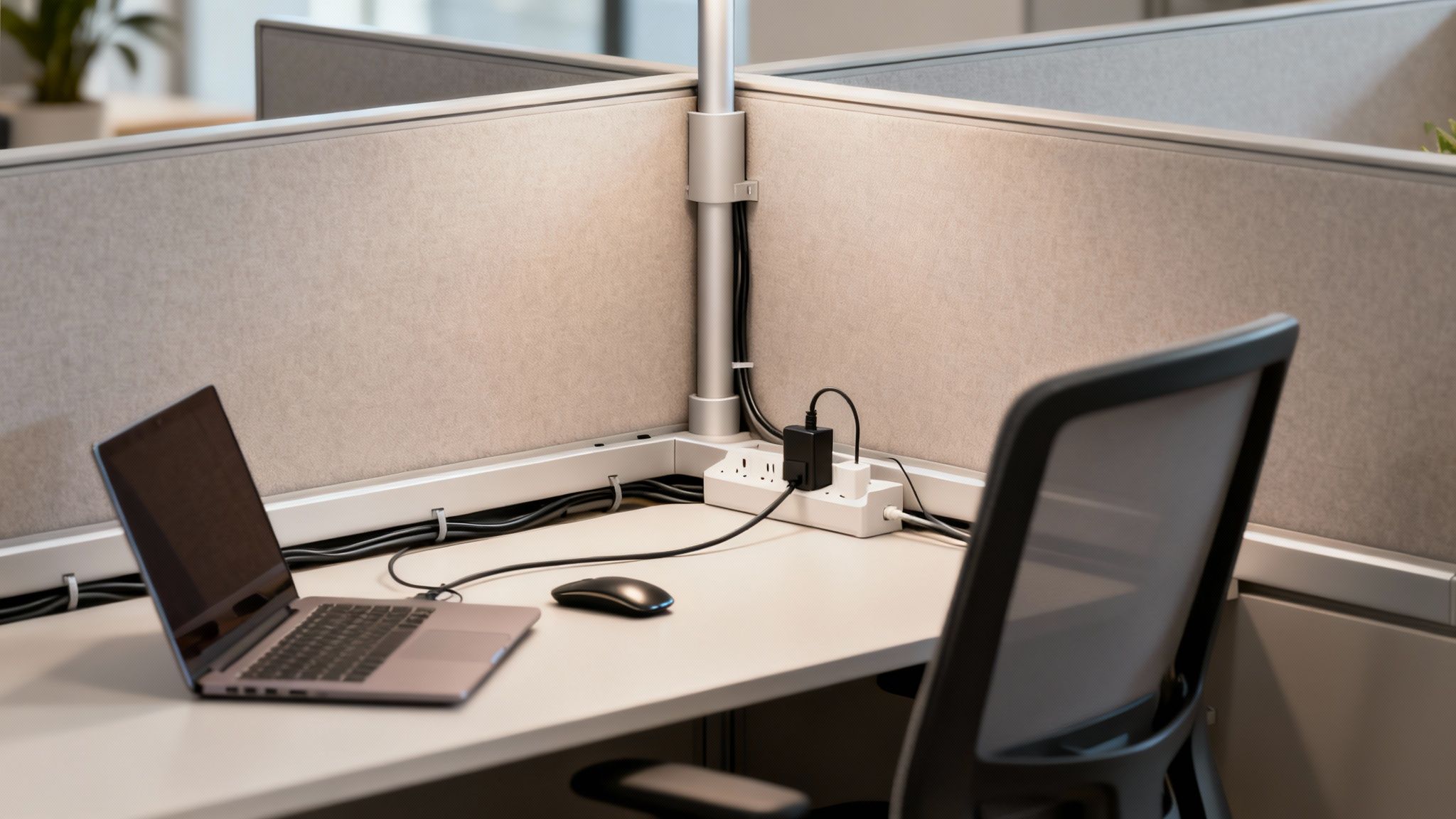

The Backbone of Office Power
Modern cubicles are engineered with power management as a core feature. They aren’t just dividers and desks—they are sophisticated systems designed to deliver electricity safely and discreetly to each workstation. This foundational power is usually handled by two key components:
- Raceways: These are the hidden channels, often found at the base of cubicle panels, that house the main electrical wiring. They act as protected conduits, keeping high-voltage cables safely enclosed and out of sight while distributing power down a whole row of desks.
- Power Poles: In open-plan offices where cubicles don’t touch a wall, power poles are the vertical channels that bring electricity down from the ceiling grid directly into the cubicle raceways. This clever solution prevents dangerous cords from being stretched across open floors.
This built-in infrastructure does all the heavy lifting, powering the core components of a workstation like the main computer tower and large monitors. It’s robust, code-compliant, and built to last.
Where the 10-Foot Power Strip Fits In
If the built-in system is the highway, then the 10-foot power strip is the local access road that gets power to specific destinations right on the desk. It provides that crucial “last-mile” connectivity for all the personal and peripheral devices your team uses every single day. This supplemental approach is what makes a workspace truly user-friendly.
To get a better handle on how these systems are planned and installed, our guide to cubicle electrical setup offers essential insights for office managers. Understanding this foundation helps you appreciate the synergy between the permanent and flexible power solutions.
This layered strategy means you don’t have to call in an electrician for disruptive, costly work every time an employee needs to plug in a new device. Instead of a major project, you simply add a power strip.
By planning your power distribution from the start, you create a workspace that is not only functional today but also scalable for tomorrow. This dual approach of integrated power plus flexible strips allows you to adapt to changing technology and team needs without a complete overhaul.
Customizing Individual Workstations
This hybrid model really shines when you start customizing different types of workspaces. For instance, in private office cubicles, the built-in power might handle the desktop computer and main task lighting. Meanwhile, a strategically placed 10-foot power strip mounted under the desk can service a laptop, phone charger, and a personal desk lamp with zero fuss.
This approach gives you the best of both worlds:
- System-Level Power: Your core electrical needs are met by a safe, permanent, and integrated system that follows all building codes.
- User-Level Flexibility: Your employees get the freedom to power their personal devices conveniently, without overloading the main circuits or creating a tangled mess of cords.
By integrating supplemental power strips into a well-planned cubicle system, you build a more functional, organized, and adaptable office environment. It’s a smart strategy that balances a robust infrastructure with the practical, everyday power needs of your team.
Your Top Questions About 10-Foot Power Strips
Even with all the technical specs figured out, real-world questions always pop up when you’re trying to get a busy office running smoothly. From what you can (and can’t) plug in to how often you need to replace them, getting straight answers is key to a safe and productive workspace.
Let’s dive into some of the most common questions we hear from office managers. Think of this as your go-to guide for those day-to-day “what-if” moments.
Can I Plug a Space Heater or Coffee Maker Into a Power Strip?
This is probably the most critical safety question we get, and the answer is a hard no. You should never plug high-wattage appliances like space heaters, coffee makers, toasters, or microwaves into any standard power strip.
These devices pull a massive amount of power—way more than your typical office gear. Plugging one in can easily overload the power strip, causing its internal wiring to overheat. This creates a serious fire hazard. The only safe way to power these appliances is by plugging them directly into a dedicated wall outlet. A 10-foot power strip is built for low-power electronics like computers, monitors, desk lamps, and phone chargers.
What Is the Difference Between a Power Strip and a Surge Protector?
They might look identical on the outside, but their internal functions are worlds apart. Understanding this difference is crucial for protecting your company’s expensive electronics.
A basic power strip is really just an extension cord with a few extra outlets. It lets you plug in more devices, but it offers zero protection against electrical surges or voltage spikes. It’s simply a pass-through for electricity.
A surge protector, however, has special internal components designed to absorb and block excess voltage during a power surge, protecting your connected equipment. For any office setup with computers, servers, or other sensitive electronics, you absolutely want a 10-foot power strip that is also a surge protector. You can tell by the “joule” rating on the packaging—the higher the joules, the more protection you get.
How Often Should Office Power Strips Be Inspected or Replaced?
Making a quick inspection part of your regular office maintenance is a smart move. At least twice a year, give every power strip a visual once-over. You’re looking for any signs of damage, like a cracked case, a frayed cord, or loose-fitting plugs.
Pay close attention to how the strip looks and feels during use. If a power strip ever feels hot to the touch or you see any discoloration or scorching around the outlets, unplug it and get rid of it immediately. Those are red flags for a dangerous internal failure.
While there’s no official expiration date, the protective bits inside a surge protector do wear out over time, especially after taking a hit from a big power spike. As a general rule of thumb, it’s a good idea to replace your office surge protectors every 3-5 years. This ensures your gear always has the protection it needs.
Is It Safe to ‘Daisy-Chain’ Power Strips?
Absolutely not. Plugging one power strip into another, or “daisy-chaining,” is never safe. This is a major fire hazard and is strictly forbidden by both OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and the National Electrical Code (NEC).
Daisy-chaining creates a massive risk of overloading the first strip and the wall outlet it’s plugged into. This can quickly lead to overheating, melting plastic, and a potential fire. If you need more outlets or a longer reach than a single 10-foot power strip offers, the only safe solution is to have a licensed electrician install more wall outlets. This is a non-negotiable safety rule for any workplace.
At Cubicle By Design, we help businesses plan their power and data needs right from the start, ensuring a safe, compliant, and efficient workspace. Whether you’re mocking up a new layout with our Cubicle Designer tool or outfitting brand-new workstation cubicles, we’ve got the expertise to get it right. From complete cubicle systems to specialized private office cubicles, all our solutions are designed with proper power management in mind.
Ready to build a smarter, safer, and more flexible workspace? The experts at Cubicle By Design can help you integrate the right power solutions for your office layout, ensuring your team has the connectivity it needs to thrive.
Explore our office furniture solutions and start planning today!
